You might have observed pushbutton switches, whether in the form of your doorbell switch or the horn switch of your car. Do you know how they work, what are the different types available, and which pushbutton you should choose as a hobbyist or engineer for your application? Our brief on pushbutton switches for a deep understanding of pushbutton switches and find answers to all the questions you may have concerning a pushbutton selection.
What is a Pushbutton switch?
A pushbutton switch is an electromechanical device used to control various functions of a machine and equipment. When pushed by the operator, this manually operated device can turn on (turn ON) or break (turn OFF) an electric circuit. You can find a pushbutton in the elevators of your building or office and in horn switches of your cars. They are generally made of plastic or metal and are available in various shapes, sizes, and configurations, depending on customer requirements.
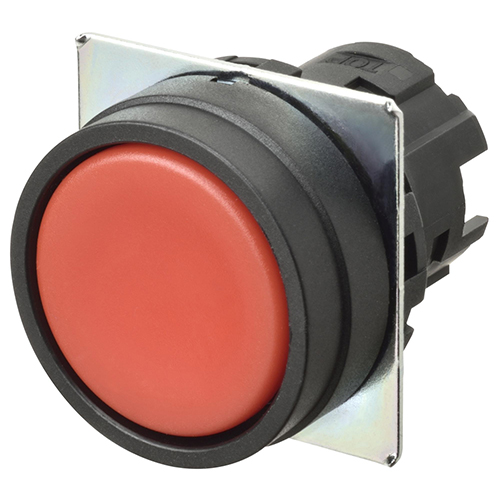

Figure 1: A pushbutton switch (Image courtesy: OMRON)
What are the main components of a switch button?
The components of a pushbutton are as follows:
- Plunger: It is made of metal or plastic and provides movement to the switch, latching the spring to open or close the contact.
- Movable spring: It assists the plunger in returning to its original position when the button is depressed.
- Terminals: These are the connection points for attaching wires using soldering, crimping, or screw method.
- Contacts: These conductive parts inside the pushbutton make or break the electrical connection when the button is pressed or released.
- Case: It encases and protects all the internal components of pushbuttons while providing structural support.
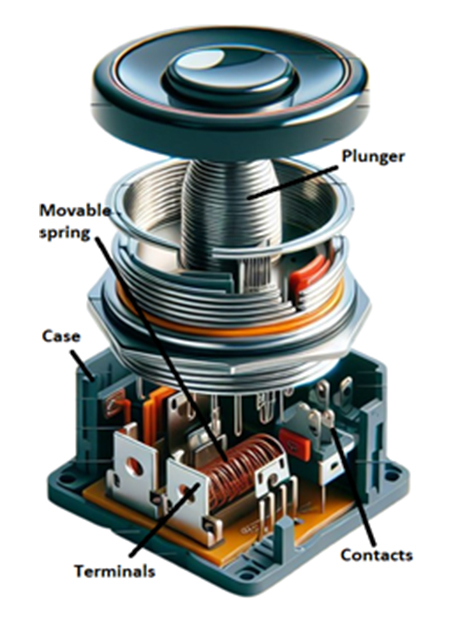
Figure 2: Components of a pushbutton switch
What is the operating principle of a pushbutton switch?
Figure 3 illustrates the working mechanism of a push button. When you press the button, a plunger attached to it moves and compresses an internal spring mechanism. This causes the movable contact to touch the fixed contacts, completing an electrical circuit. When you release the button, the spring returns to its original position and disconnects the circuit.
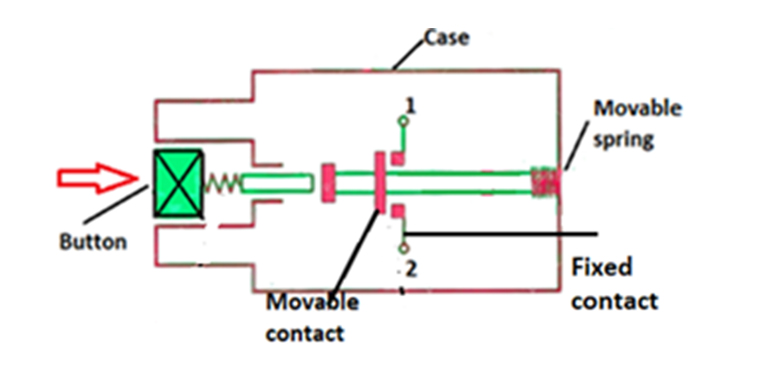
Figure 3: Illustration of working mechanism of a pushbutton switch
Momentary and Maintained Pushbutton
- Momentary pushbutton: “Momentary” means the action lasts only for a moment. These push buttons are actuated only as long as they are pressed. If you remove the pressure from the pushbutton, it will be deactivated. A very popular example of this type of button is your doorbell switch.
- Maintained pushbutton: When you press a maintained pushbutton, it gets actuated and remains in the same state. It has a latching mechanism that maintains the actuated state, even if you release the finger from the button. To deactivate this pushbutton, it must be pressed again to release the latch. A common example of this is the power button of your computer.
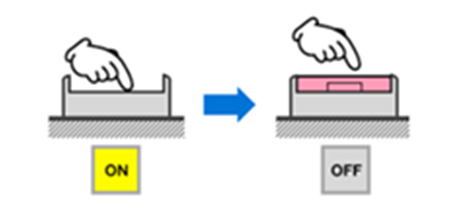
Figure 4: Operation of a momentary pushbutton (Image courtesy: OMRON)
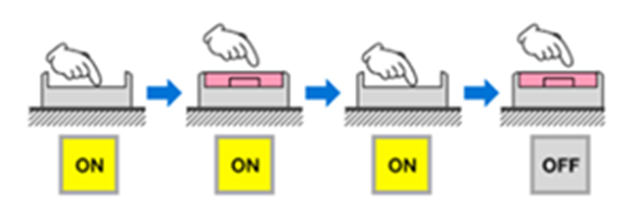
Figure 5: Operation of a maintained pushbutton (Image courtesy: OMRON)
Normally open and normally closed pushbutton
- Normally Open (NO) pushbutton: In a normally open push button, the contacts are open when the button is not pressed, and the switch maintains the open (OFF) condition. When the push button is pressed, the contacts are closed, and the condition of the switch turns to close (ON).
- Normally Closed (NC) pushbutton: In a normally closed pushbutton, the contacts are closed when the button is not pressed, maintaining the closed (ON) condition. When the push button is pressed, the contacts open, and the switch changes to open (OFF) condition.
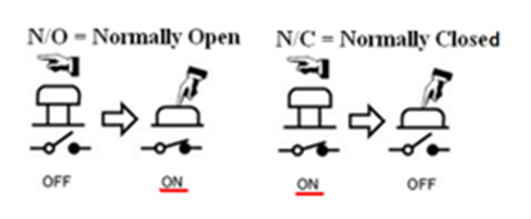
Figure 6: Operation of NO and NC pushbuttons (Image courtesy: NKK Switches)
What is an emergency stop pushbutton?
Emergency stop switches, or E-stop pushbuttons, are electromechanical switches used to safely shut down machines or stop processes. They are essential in automated machines and plants to prevent personal injury and material loss. These are similar to a kill switch on your motorcycle. There are several types of E-stop pushbuttons. The most popular are palm- or mushroom-shaped, red, and yellow, making them easily identifiable by operators.
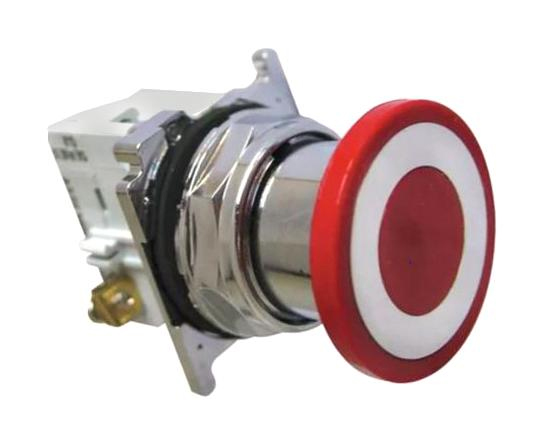

Figure 7: E-stop switch (Image courtesy: Eaton)
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) on Pushbuttons
What is the purpose of an anti-vandal pushbutton?
An anti-vandal pushbutton is designed to provide robust performance and rugged protection from harsh environments like dust and moisture and deliberate attempts of tampering or vandalism. These switches are commonly used in applications like intrusion detection, vending machines, ATMs, where durability and security are crucial.
What is an illuminated pushbutton?
An illuminated push button incorporates visual indicators (an LED or a neon lamp) to provide visual feedback or the status of the switch (ON or OFF). It provides an ergonomic and visual interface for precise control of machines. It is easily distinguishable at a distance in low-light conditions. A common example of an illuminated pushbutton is the buttons present in elevators.
What are the various applications of pushbutton switches?
Pushbuttons and switches are widely used in domestic and industrial applications. At home, they are used to operate your computer, doorbell, washing machine and even to flush your toilets. In industrial applications, they are used to operate power tools and machinery and for process control. Pushbutton switches are also used in telecommunications, automotive, medical applications.
Are there any IP-rated pushbutton switches also available?
Yes, pushbuttons with IP ratings of 40, 54, 67, and 68 can be installed in many outdoor heavy-duty applications. A button with an IP40 rating will be protected against solid objects but not liquids. An IP54-rated button is protected from a limited amount of dust and splashes of water from all directions. Similarly, the IP67 rated pushbutton can withstand all types of dust and survive in water for 30 minutes at a depth of about 3 feet. A pushbutton with an IP68 rating provides protection against various dust types and will continue to function when submerged in water to a depth of 4 meters.
Is there any significance of pushbutton shapes?
Pushbuttons are available in different shapes, not for aesthetic reasons but because some ergonomics and durability factors. The switch with a flush actuator protects against accidental actuation, and therefore, used in situations where pressing the switch can cause something potentially dangerous to happen. Round-head pushbuttons have a user-friendly design. They are ideal for applications where rapid response is essential, such as turning a machine on and off. The rectangular and square heads feature a wider and more comfortable pressing surface. They are used in consumer electronics and home automation applications.
Where can I buy pushbuttons at the best price?
Farnell Electronics offers a comprehensive range of pushbutton switches tailored for automotive, consumer electronics, and industrial applications at the best price from leading suppliers. The product line includes pushbuttons with different IP ratings, shapes and options.













